

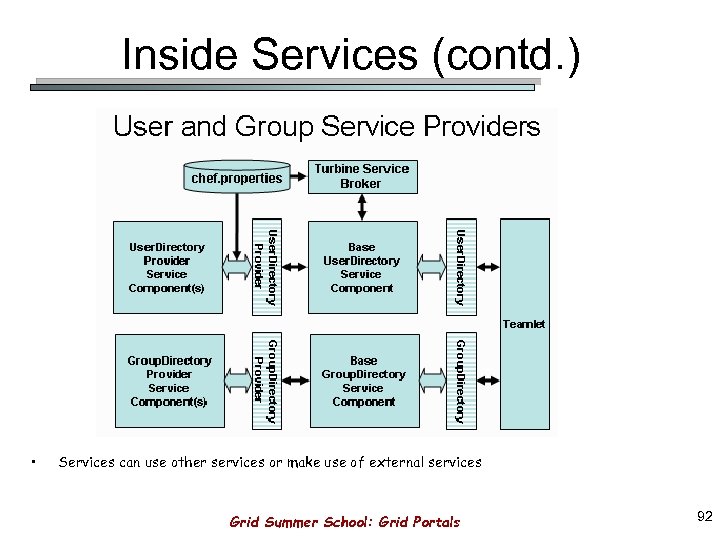
In database replication, the systems store copies of data on different sites. The following diagram shows an example of a heterogeneous database: Distributed Database Storageĭistributed database storage is managed in two ways: The limitation is why translations are required to establish communication between sites. In the case of a heterogeneous distributed database, a particular site can be completely unaware of other sites causing limited cooperation in processing user requests. The following diagram shows an example of a homogeneous database: HeterogeneousĪ heterogeneous distributed database uses different schemas, operating systems, DDBMS, and different data models. Homogenous databases allow users to access data from each of the databases seamlessly. The sites have the same operating system, DDBMS, and data structure, making them easily manageable.

There are two types of distributed databases:Ī homogenous distributed database is a network of identical databases stored on multiple sites. Transaction processing is an atomic process that is either entirely executed or not at all. Transaction processing - Distributed databases incorporate transaction processing, which is a program including a collection of one or more database operations.Network linking - All databases in a collection are linked by a network and communicate with each other.Seamless integration - Databases in a collection usually represent a single logical database, and they are interconnected.Distributed transaction management - Provides a consistent distributed database through commit protocols, distributed concurrency control techniques, and distributed recovery methods in case of many transactions and failures.High-level queries are transformed into a query execution plan for simpler management. Distributed query processing - Distributed databases answer queries in a distributed environment that manages data at multiple sites.Location independency - Data is physically stored at multiple sites and managed by an independent DDBMS.Some general features of distributed databases are: DDBMS synchronizes all data operations among databases and ensures that the updates in one database automatically reflect on databases in other sites. More nodes in the system provide more computing power, offer greater availability, and resolve the single point of failure issue.ĭifferent parts of the distributed database are stored in several physical locations, and the processing requirements are distributed among processors on multiple database nodes.Ī centralized distributed database management system ( DDBMS) manages the distributed data as if it were stored in one physical location. They scale horizontally and develop a distributed system. Since the databases are all connected, they appear as a single database to the users.ĭistributed databases utilize multiple nodes. Distributed Database DefinitionĪ distributed database represents multiple interconnected databases spread out across several sites connected by a network. In this article, you'll learn what distributed databases are and their advantages and disadvantages. Some more advanced photocopiers have a ‘single pass’ document feeder, which can scan in double-sided paper in one pass, as opposed to making the paper go around twice.Distributed databases are used for horizontal scaling, and they are designed to meet the workload requirements without having to make changes in the database application or vertically scale a single machine.ĭistributed databases resolve various issues, such as availability, fault tolerance, throughput, latency, scalability, and many other problems that can arise from using a single machine and a single database. Paper documents are drawn into the top of the feeder by a set of rollers, which then feed it through to pass through a smaller piece of glass (called the slit glass) which scans in the paper before it’s placed in the exit tray on the feeder. The automatic document feeder can be used to scan a large number of files very quickly. The platen glass has a large surface area. The platen glass is used to scan in single documents, or multiple documents which need to be integrated into the same copy or file.
On a standard office photocopier, you can normally find both a normal scanner under the lid of the copier, called the ‘platen glass’ and an ‘Automatic Document Feeder’, which is based on the very top of the device. This allows paper documents to be turned into various types of digital file which can then be used to store on a computer, or even imported into your business Document Management System. Your photocopier’s scanner can scan in single documents in the same way a normal standalone scanner can, but it can also scan whole stacks of paper in bulk.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
